Fred McGriff is a victim. He is a victim of an overcrowded ballot, causing writers to leave players off their ballot they find worthy of a vote. He is the victim of the era he played in; his numbers overshadowed by players who were juicing, making McGriff’s numbers look more run-of-the-mill than they should have. It is time to start giving the “Crime Dog” the respect he deserves.
500 Home Runs
Remember when 500 home runs used to gain someone automatic induction into the Hall of Fame. The steroid era hit and that all changed as baseballs started flying out of parks at historic rates. How come the standards shouldn’t remain the same for someone who played the game clean though? If they never used steroids, they weren’t getting that extra help in hitting home runs and 500 should remain a significant threshold.
McGriff didn’t hit 500 home runs, but his 493 is tied with Lou Gehrig for the most home runs by a player with less than 500. Would hitting seven more home runs change the kind of player Fred McGriff was? Of course not. If falling seven home runs shy of 500 is helping keep his votes down, that is just ridiculous. That would be saying if McGriff had hit one more home run every two years, he was more worthy of being a Hall of Famer.
McGriff would have surely reached 500 career home runs if not for the strike. When the strike happened in mid-August, McGriff had 34 home runs. With a month and a half to go he would surely have hit seven more homers. The strike lasted until late April the following season, costing him even a few more games. It is likely that without the strike he would have wound up right around Eddie Murray’s 504 career home runs.
Speaking of Eddie Murray, who coasted into the Hall of Fame on his first ballot, check out their career numbers. Besides the hit totals, McGriff’s career statistics compare pretty well to Murray’s. Murray had nearly 3000 more at-bats, so he gained more counting numbers. The home runs are similar and McGriff has the better on-base percentage and slugging percentage, topping him by 50 OPS points. I am not saying Fred McGriff was better than Eddie Murray, I do not believe that. The distance between the two might not be as large as you think though.

In 1994-95, McGriff averaged a HR every 15.6 at-bats. He would have surpassed 500 home runs if not for the strike costing him 2 months.
The Difference in Eras
When McGriff first came up with Toronto in the eighties, he was one of the biggest power hitters in the game. He hit 20 home runs in only 295 at-bats in 1986. He proceeded to eclipse 30 home runs in each of the next seven seasons. McGriff led the league in home runs in both 1989 with the Blue Jays and 1992 with the Padres. In the late 80’s and early 90’s hitting 35 home runs meant you led the league or came close. By the mid to late 90’s his 30 home runs were lost in the shuffle of steroid hitters. Illustrating this point, McGriff finished in the top five in the league in home runs all seven seasons from 1988-1994. He never finished in the top 10 again.
If McGriff had come along a decade earlier he would already be in the Hall of Fame. Instead, over eight years he has yet to accrue even 25 percent of the vote. Based on what he did prior to the steroid era, he would be a Hall of Famer. Explain to me how the steroid era is counted against him when he never used steroids? Not only did he not benefit from steroids, he was going against stiffer competition, playing on an uneven field. Once all the steroid facts came out my opinion of McGriff went up. There is no proof, or even any evidence that he ever used, he just had the misfortune of being a power hitter in that era.

Fred McGriff of the Toronto Blue Jays bats against the Chicago White Sox during a Major League Baseball game circa 1986 at Comiskey Park. (Photo by Focus on Sport/Getty Images)
No Steroids
As I said previously, there is no reason for anyone to suspect McGriff of steroid use. First off, he never got bigger. Check the pictures of McGriff through the years, he looks the same in Atlanta as he did in Toronto, and he looks the same in Tampa Bay as he did in Atlanta. His head never grew larger, his neck never got huge, and his upper body never became strikingly larger. He was always a tall, slender first baseman.
Secondly, McGriff’s home runs never spiked. In fact, he hit more home runs in the first half of his career before the steroid era really struck than he did during the peak of steroid use. From 1987-1994 he averaged 33 home runs per season, 38 per 162 games played. From 1992-2002, his last good season, he averaged 27 home runs per season, 30 per 162 games. If you want to cut a couple years off earlier in his career, he still averaged 36 home runs per 162 games played the first six seasons of his career.

23 Apr 1998: Infielder Fred McGriff of the Tampa Bay Devil Rays in action during a game against the Texas Rangers at The Ball Park in Arlington, Texas. The Devil Rays defeated the Rangers 12-5. Mandatory Credit: Stephen Dunn /Allsport
The Postseason
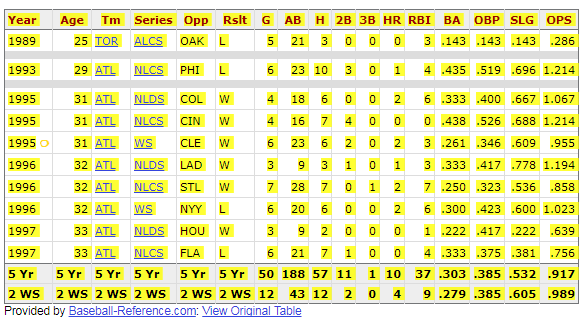
Fred McGriff has a large collection of playoff data to his resume. He was traded for by Atlanta prior to the trade deadline in 1993 to help fortify their lineup. He caught fire for Atlanta, hitting 19 home runs and posting a 1.004 OPS after the trade. The Braves went 50-17 after the trade and edged out the Giants for the division title by one game. McGriff then batted .435 with a 1.214 OPS in the playoffs that year.
The Braves would have made the playoffs if not for the strike in 1994. McGriff then made three consecutive postseasons with the team before heading to Tampa Bay. In 1995 the Braves finally got their World Series title, with McGriff belting two home runs during the series. For that postseason he batted .333 with four home runs. In total, McGriff played in 50 postseason games, batting .303 with 10 home runs and a .917 OPS. Postseason results are taken into account for other players, and McGriff certainly proved to be a good postseason performer.
Advanced Metrics
The new age “statistics” don’t help McGriff get votes from the writers who buy into those more than actual statistics. Those “new age statistics” are not fair to someone who played clean during the steroid era though. WAR and OPS+ take into account the average player’s numbers and adjust a players OPS or calculate their value comparatively. In an era matched up against juiced players, how is it fair to use a juiced players totals against a clean player? Everyone wants to vilify steroid users and pretend they weren’t a part of the game, keeping them out of the Hall of Fame. So let me get this straight, if you used steroids it is counted against you, but if you didn’t use steroids…it’s counted against you?
From 1988-94, the first seven full seasons of his career, McGriff posted a 155 OPS+. With those unfamiliar with the stat, that is a very high number. To put things into perspective, Hank Aaron, Joe DiMaggio and Mel Ott had career OPS+ of 155. Those are three of the greatest to ever play the game. McGriff twice had an OPS+ of 165 and never dipped below 144 during those seasons. From 1995 on he was typically between 106-120, good, but not outstanding. However, that is because he was being judged against a large number of performance enhancers. Posting those same numbers several years earlier likely would have resulted in an OPS+ of 140 or better each season.
Conclusion
It is clear that going onto his ninth ballot McGriff will not earn induction during his voting window. My belief is he will eventually get recognized by the Modern Era Committee and earn enshrinement down the road. You cannot hold steroid use against players who used but then use their numbers as an argument against someone who played the game clean. The Hall of Fame needs to fix the voting system, the ballot is a total mess. The writers also need to do a better job of looking at someone who played the game clean and not using their era against them. Not to mention, the “Crime Dog” moniker is worthy of the Hall of Fame in itself.
